What is Inspiratory Muscle Training?
What is Inspiratory Muscle Training?
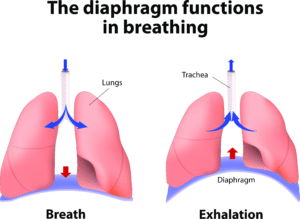
As part of Respiratory Muscle Training (RMT), Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT) strengthens the muscles of inhalation specifically. This method focuses on deep diaphragmatic breathing against resistance. During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and descends into the abdominal cavity, thereby expanding the lungs’ volume. At the same time, the chest wall (intercostals) and accessory neck and shoulder muscles move to raise the ribs and sternum to further increase the lung volume during inhalation.
Mechanism of IMT
Just like with any other exercise, before starting IMT, the respiratory baseline should be assessed to tailor the individual approach and intensity of training. Then, the respiratory muscles are exercised by working against a set resistance, putting a target workload on the muscles.
IMT on Delaying Metaboreflex

As oxygen supply is limited, the body is faced with the decision to either continue supplying the working muscles (e.g. running) or to keep breathing. As breathing is always prioritized, the body redirects blood flow from the exercising muscles to the respiratory muscles. At this point, the breathing muscles also fatigue from the exercise, demanding more oxygen than before, and using up more of the supply. IMT helps to delay respiratory muscle fatigue and the onset of the metaboreflex.
Benefits of IMT

Besides pushing performance, more effective breathing muscles also help to relax and unwind from a stressful situation. As IMT trains diaphragmatic breathing, this natural and effective breathing pattern becomes a habit again. While diaphragmatic or belly breathing is the natural breathing pattern that we are born with, most people switch to shallow and ineffective chest breathing as they grow up. Resetting the breathing pattern and strengthening the respiratory muscles by IMT helps to promote natural breathing, and activates the parasympathetic nervous system associated with a calm and relaxed state. IMT can improve quality of life, sleep, and impacts on every aspect of life.
The unique position of the diaphragm within the body makes it a respiratory muscle and a component of core strength and posture. Strengthening the diaphragm through IMT, therefore promotes balance, core stability, and posture, and can contribute to reduced injury risk.
Recommendation


